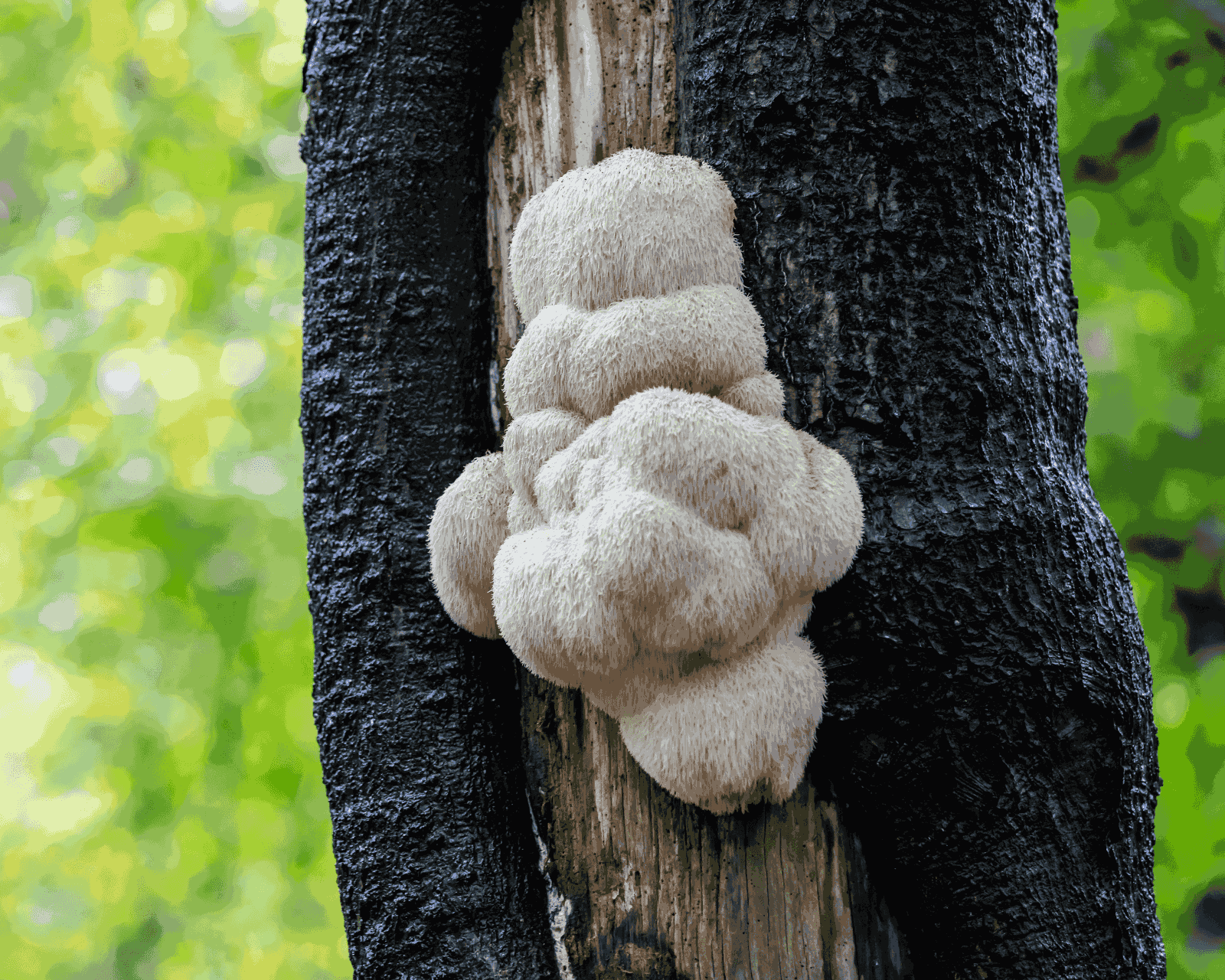
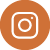
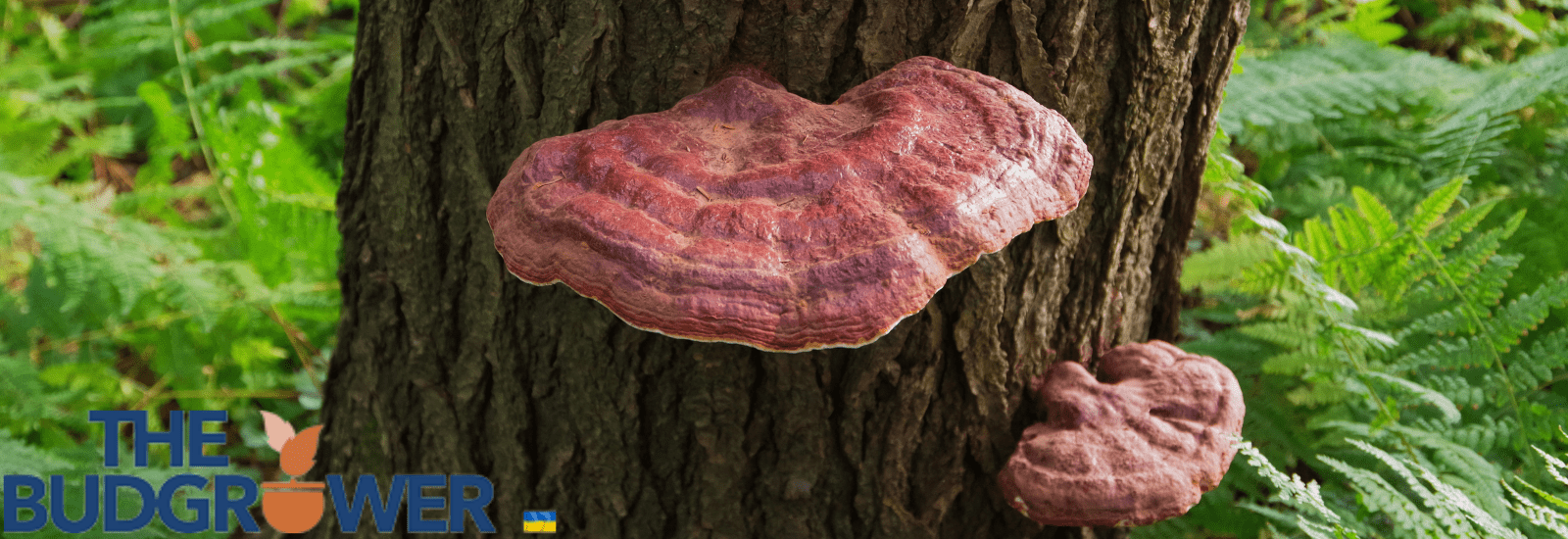
Tree mushrooms are the fungi that often grow on the wood (bark) of living or dead trees. The mycelium grows on the tree’s wood, and when favorable conditions arise, mushrooms sprout from these bodies.
These mushrooms feed on the nutrients absorbed from trees’ bodies and roots. Mostly, they have a symbiotic relationship with trees, in which they do not harm their host tree but decompose (deadly) wood. Other times, they have a parasitic relationship with the trees they grow on.
In that case, they damage the trees and harm their growth. This blog will discuss the major reasons for mushroom growth on trees and how you can identify it.
Reason for the Growth of Mushrooms on Trees
Wood-decaying fungi, or tree mushrooms, grow on trees with considerable decaying organic matter. Trees with any disease or damage favor the growth of fungi as well.
Sometimes, they manage to get inside the trees via wounds or injuries. They cause the mycelium to grow, which feeds on the cellulose (a material in plants’ wood).
When the weather conditions, e.g., rain, high temperature, etc., are optimal, mushrooms fruit out of mycelium and appear on the trees’ bark.
How Can You Identify If There Are Mushrooms on Trees?
Tree mushroom identification can be tricky. Some various signs and systems can suggest the presence of mushrooms on trees.
Mycologists suggest that if you find any of the following symptoms, there is a possibility that fungus is growing on the tree:
Discoloration or Change of Wood Color
One of the common signs is the change in color of trees’ wood, e.g., black or dark brown. Sometimes, the bark can become discolored.
This is because the mushrooms decay the organic matter from the wood, leaving it in such colors.
Sprouts on the Tree Trunk
The presence of sprouts or fruiting bodies on the tree trunk, branches, or anywhere else clearly indicates that the mushrooms are about to grow on the respective tree.
These sprouts seem so fascinating and attractive to the eyes, but to their host trees, they are alarming.
Cracked Trunk Texture
If the trunk appears to be rougher, damaged, or cracked than usual, there is a possibility that mushrooms are growing on that tree.
Because mycelium seeps inside the trunk, it causes damage to its texture. Over the years, the trunk becomes lifeless.
 Types of Mushrooms That Grow on Trees
Types of Mushrooms That Grow on Trees
Different types of mushrooms can be found on trees. They can be categorized based on their structure and relationship with their host trees.
Types Based on Structure
There are three types of fungus on trees, based on what they look like:
1. Bracket or Shelf Mushrooms
They look like shelves or brackets on the trees. They are primarily leathery or woody in texture.
They decay wood and are thus suitable for decomposing lifeless timber. They come in a wide variety of sizes, shapes, and colors. Turkey tail and maitake mushrooms are prominent examples.
2. Jelly Like Mushrooms
As the name suggests, they are translucent mushrooms that appear to be made of gelatin or rubber.
They are of different sizes and shapes, mostly found attached to the trunk or branches of the trees. Wood ear and witches butter fall under this category of mushrooms.
3. Cap Mushrooms
These are the commonly found mushrooms with a flat cap attached to the stem. Some of these are polypores, which have pores under their caps.
Examples of these mushrooms include oyster mushrooms and honey mushrooms.
Types Based on Relationship with Trees
1. Parasitic Mushrooms
These mushrooms act as parasites on their host trees, causing damage to them. They absorb all the nutrients from their hosts and suck out all the strength from the trees, leaving them dead or decayed.
This relationship is beneficial for mushrooms but harmful for trees. Cauliflower mushrooms, white mushrooms, and honey mushrooms are some good examples.
2. Mycorrhizal Mushrooms
These mushrooms build a symbiotic relationship with their host’s roots-like structures, called mycorrhiza. This relationship is advantageous to both of them.
The mushrooms get their food from the tree they are on, and in return, they help trees access more nutrients and absorb more water from the soil. Prized truffles and fly algaric fall under this category of mushrooms.
 Uses of Tree Mushrooms
Uses of Tree Mushrooms
Mushrooms are helpful in many ways. Two of the most common uses are:
Edible Mushrooms
Many mushrooms are edible and can be used as food. They can have different tastes, smells, and sizes. Many mushrooms are named after how they taste or look.
Beefsteak (which resembles meat in color and texture), Hen of Wood, Shiitake, and Chicken of Wood (which tastes like chicken) are some examples of edible mushrooms.
Medicinal Mushrooms
Some mushrooms are used for medicinal or therapeutic purposes. This is one of the main reasons why many foragers and growers harvest mushrooms if it is legal in their state. Some prominent examples include Reishi, Turkey Tail, and Lion’s Mane.
Advantages of Tree Mushrooms
Mushrooms have many advantages, especially from a biological point of view, as they play a significant role in purifying the ecosystem. The advantages include:
- Decomposition of dead wood
- Recycling of nutrients in soil
- Maintain a healthy ecosystem
Conclusion
Whether you are thinking about growing mushrooms in your home or garden or using them for medicinal purposes, always consult a mycologist for tree mushroom identification.
You should be aware of potential risks and concerns when dealing with mushrooms, as they can be poisonous.